WTF Solidity: 2. Value Type
Recently, I have been revisiting Solidity, consolidating the finer details, and writing "WTF Solidity" tutorials for newbies.
Twitter: @0xAA_Science | @WTFAcademy_
Community: Discord|Wechat|Website wtf.academy
Codes and tutorials are open source on GitHub: github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity
Variable Types
Value Type:This include boolean, integer, etc. These variables directly pass values when assigned.
Reference Type:including arrays and structures. These variables take up more space, directly pass addresses (similar to pointers) when assigned, and can be modified with multiple variable names.
Mapping Type: hash tables in Solidity.
Only the commonly used types will be introduced here. In this chapter, we will introduce value types.
Value types
1. Boolean
Boolean is a binary variable, and its values are true or false.
// Boolean
bool public _bool = true;
Operators for Boolean type include:
!(logical NOT)&&(logical AND)||(logical OR)==(equality)!=(inequality)
Code:
// Boolean operators
bool public _bool1 = !_bool; // logical NOT
bool public _bool2 = _bool && _bool1; // logical AND
bool public _bool3 = _bool || _bool1; // logical OR
bool public _bool4 = _bool == _bool1; // equality
bool public _bool5 = _bool != _bool1; // inequality
From the above source code:the value of the variable _bool is true; _bool1 is not_bool, which yields false; _bool && _bool1 is false;_bool || _bool1 is true;_bool == _bool1 is false;and _bool != _bool1 is true.
Important note: The && and || operator follows a short-circuit evaluation rule. This means that for an expression such as f(x) || g(y), if f(x) is true, g(y) will not be evaluated.
2. Integers
Integers types in Solidity includes signed integer int and unsigned integer uint. It can store up to a 256-bit integers or data units.
// Integer
int public _int = -1; // integers including negative numbers
uint public _uint = 1; // non-negative numbers
uint256 public _number = 20220330; // 256-bit positive integers
Commonly used integer operators include:
- Inequality operator (which returns a Boolean):
<=,<,==,!=,>=,> - Arithmetic operator:
+,-,*,/,%(modulo),**(exponent)
Code:
// Integer operations
uint256 public _number1 = _number + 1; // +, -, *, /
uint256 public _number2 = 2**2; // Exponent
uint256 public _number3 = 7 % 2; // Modulo (Modulus)
bool public _numberbool = _number2 > _number3; // Great than
You can run the above code and check the values of each variable.
3. Addresses
Addresses have following 2 types:
address: Holds a 20 byte value (size of an Ethereum address).address payable: Same asaddress, but with the additional memberstransferandsendto allow ETH transfers.
Code:
// Address
address public _address = 0x7A58c0Be72BE218B41C608b7Fe7C5bB630736C71;
address payable public _address1 = payable(_address); // payable address (can transfer fund and check balance)
// Members of address
uint256 public balance = _address1.balance; // balance of address
4. Fixed-size byte arrays
Byte arrays in Solidity come in two types:
- Fixed-length byte arrays: belong to value types, including
byte,bytes8,bytes32, etc, depending on the size of each element (maximum 32 bytes). The length of the array can not be modified after declaration. - Variable-length byte arrays: belong to reference type, including
bytes, etc. The length of the array can be modified after declaration. We will learn more detail in later chapters
Code:
// Fixed-size byte arrays
bytes32 public _byte32 = "MiniSolidity";
bytes1 public _byte = _byte32[0];
In the above code, we assigned value MiniSolidity to the variable _byte32, or in hexadecimal: 0x4d696e69536f6c69646974790000000000000000000000000000000000000000
And _byte takes the value of the first byte of _byte32, which is 0x4d.
5. Enumeration
Enumeration (enum) is a user-defined data type within Solidity. It is mainly used to assign names to uint, which keeps the program easy to read.
Code:
// Let uint 0, 1, 2 represent Buy, Hold, Sell
enum ActionSet { Buy, Hold, Sell }
// Create an enum variable called action
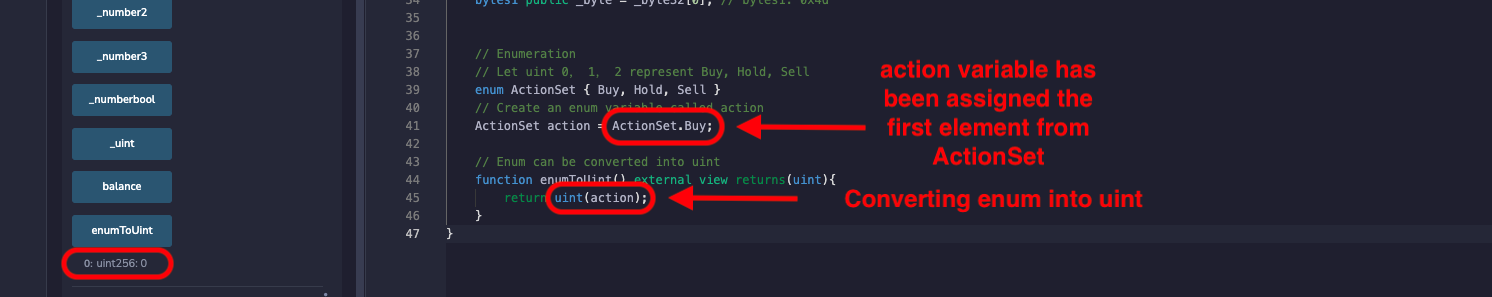
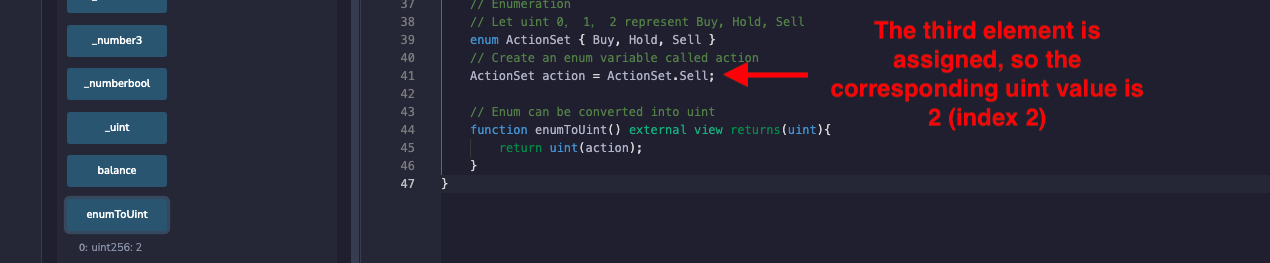
ActionSet action = ActionSet.Buy;
It can be converted to uint easily:
// Enum can be converted into uint
function enumToUint() external view returns(uint){
return uint(action);
}
enum is a less popular type in Solidity.
Demo in Remix
After deploying the contract, you can check the values of each variable:
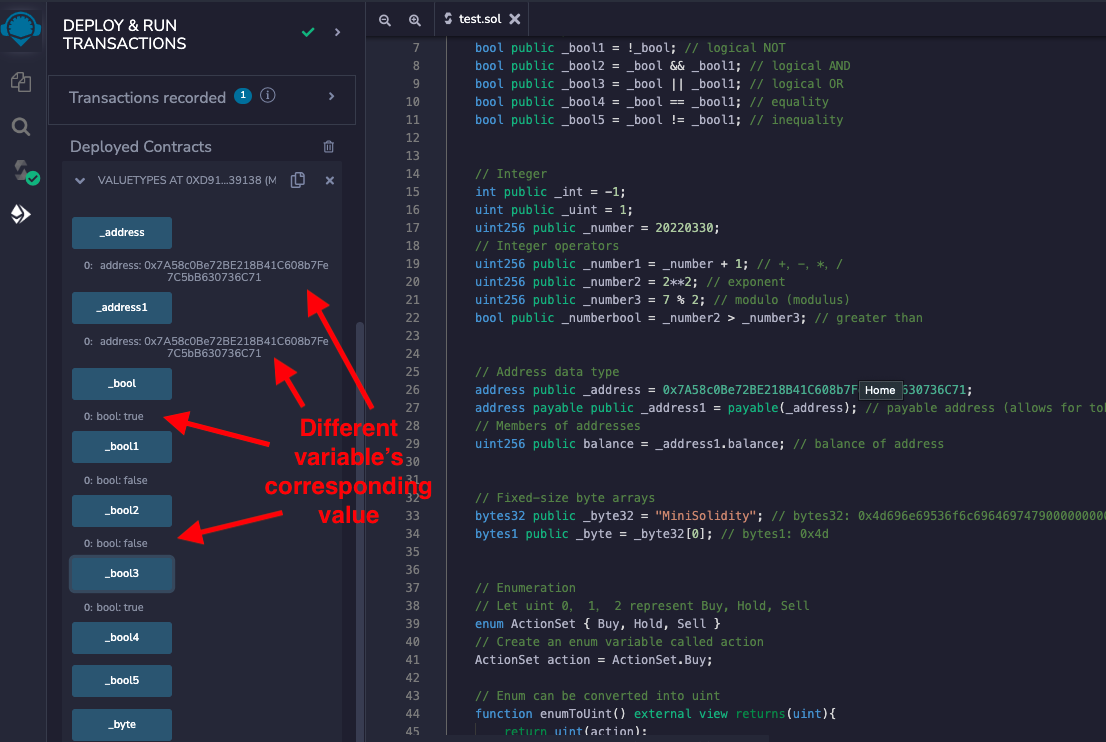
Conversion between enum and uint:
Coding Exercise
SoLive The first open-source lightweight Solidity IDE that can be easily integrated into websites, documents, and tutorials. Powered by WTF Academy, Inspired by Remix-IDE and react-live.
Try to complete the following contract and make it compile!
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.4;
contract Quiz2{
// add something here
bool public _bool =
string public _string =
bytes32 public _byte32 =
address public _address =
// make DirectionSet contain East, South, West, North.
enum DirectionSet =
}
Summary
In this chapter, we introduced the variable types in Solidity, they are value type, reference type, mapping type, and function type. Then we introduced commonly used types: boolean, integer, address, fixed-length byte array, and enumeration in value types. We will cover other types in the subsequent tutorials.